
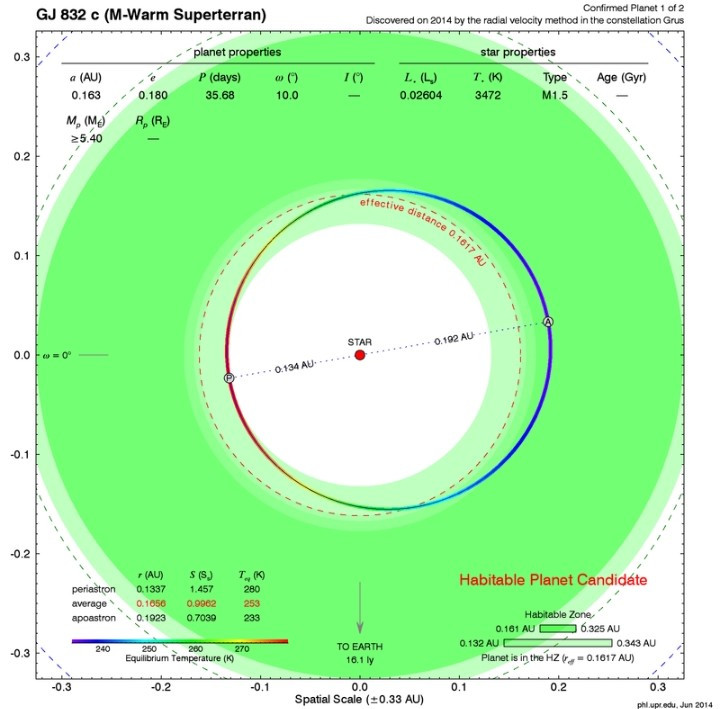
Gliese 832c (also known as GI 832c or GJ 832c) is an extrasolar planet located approximately 16 light years away in the constellation of Grus, orbiting the star Gliese832, a red dwarf.
The planet, GJ832c, has a mass at least five times that of Earth.It is among the top three most Earth-like exoplanets ever discovered. The “super-Earth” planet, Gj832c, takes 16days to orbit its red-dwarf star,Gj832.
It receives about the same average stellar energy as Earth does, because red dwarfs shine more dimly than our Sun, and may have similar temperatures to our planet.
These characteristics put it among the top three most Earth-like planets, according to the Earth Similarity Index developed by scientists at the University of Puerto Rica in Arecibo.
Their data were combined with observations from the 6.5m Mangellan Telescope and the European Southern Observatory 3.6m Telescope (both in Chile) to make this new discovery.
On the Earth Similarity Index, or ESI, the highest ranking exoplanet is Gliese 667C c, which is about 23 light years away. It has an ESI of 0.84 compared to Earth’s maximum score of 1.0.
Next on the list is Kepler-62 e with an ESI of 0.83, although it is much further away – about 1,200 light years distant. And the new planet- the closest at just 16 light years away- comes in third with an ESI of 0.81.

“However, given the large mass of the planet, it seems likely that it would possess a massive atmosphere, which may well render the planet inhospitable. A denser atmosphere would trap heat and could make it more like a super-Venus and too hot for life,” said Professor Tinney.